Agar or agar-agar is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from “ogonori” (Gracilaria) and “tengusa” (Gelidiaceae). As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose.
Gracilaria red algae

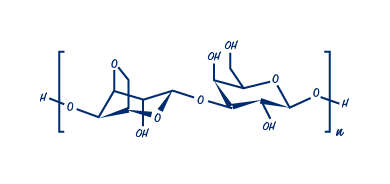
Molecular Structure
Agar consists of a mixture of two polysaccharides: agarose and agaropectin, with agarose making up about 70% of the mixture, while agaropectin makes about 30% of it.
Properties
Agar, when mixed with water, solidifies and forms a gel at about 32–42°C, which is called the gel point, and melts at 85°C, which is the melting point. This property lends a suitable balance between easy melting and good gel stability at relatively high temperatures. Since many scientific applications require incubation at temperatures close to human body temperature (37°C), agar is more appropriate than other solidifying agents that melt at this temperature, such as gelatin.
Uses
This hydrocolloid is primarily used for its gelling properties. About 90% is used in food applications, with the remaining 10% intended for bacteriological and other biotechnology applications.
Agar has the E Number E 406.
Food
Generally, agar is used in jelly, bakery, confectionery, dairy products, beverages, meat products etc.
Jelly
The most use of agar is in jellies and other desserts that need to gel. In Asian countries, agar is a traditional and popular component of jellies. For producing jellies and puddings, agar is boiled in water first, making it completely soluble, then colours, flavours, sweeteners and fruits are added to the liquid before cooling and finally pouring the liquid mix into moulds to form a jelly.
Bakery
In the baking process, it stabilizes and thickens pie fillings, sugar icings, bread dough, cake glazes, coatings and meringues with the property of withstanding high temperature.
Confectionery
Nowadays, agar from Gracilaria is often used in confectionery with high sugar content, such as fruit candies, gummies, gums, caramels, marshmallows and etc.
Dairy Products
Agar can be used in dairy products like yogurts, ice cream, cheese, chocolate and etc.
Beverage
It acts as a clarifying and refining agent for juices, beers and wines.
Meat Products
Agar is also used to gel meat and fish products, and function as a gelatin substitute for its higher melting temperature and gel strength.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, it can function as binding, masking and viscosity controlling agents in cosmetic and personal care products.
Pharmaceuticals
It is a soluble dietary fiber and has the health benefits used as a mild laxative in the treatment of malfunctions of the digestive tract for its swelling properties.
Others
Agar is used as a solidifying agent in bacteriological culture media.
